Seized motorcycle engine: symptoms, actions, and prevention
The connecting rod is a crucial component of a motorcycle's engine. It connects the crankshaft to the piston, converting the piston's vertical motion into the crankshaft's rotational motion. When an engine seizes, it means that there is severe damage to the connecting rod, ranging from crack formation to complete breakage, affecting other engine components as well. This issue often arises from deformations, detachment from its housing, or a complete breakage of the connecting rod. A seized motorcycle engine or having a seized crankshaft carries serious risks as it can cause significant damage to multiple components and even lead to piston failure.
Sometimes the problem manifests gradually, allowing for timely action to avoid serious damage, while other times failure is immediate. Typically, a seized or near-seized engine can be identified by an unusual noise: a metallic rattling sound caused by deformation of the connecting rod or bearings. Let's explore the risky behaviors to avoid, what to do in case of a seized engine, and the potential costs of repair.

A seized motorcycle engine is a critical issue
Fortunately, a broken connecting rod, while severe, is a relatively rare malfunction. It usually occurs when the engine is subjected to frequent "over-revving," exceeding the maximum RPM allowed. This can happen due to persistent lubrication problems or a combination of the two factors. Lubrication is vital in reducing friction between engine components and protecting against excessive heat. Without proper lubrication, the engine is at risk of seizing, especially during dreaded "over-revving in downshifting.” This occurs when downshifting too many gears simultaneously, causing the engine RPMs to surge well beyond the maximum limit allowed due to the inertia of the moving mechanical parts, posing severe risks to the engine's integrity.
This also happens when motorcycle maintenance intervals are not respected, or the vertical clearance of the connecting rod is not checked (moving it upwards should not produce any noise or tapping; if it does, the connecting rod head itself may fail). Motorcycle maintenance intervals are determined based on either engine running time or mileage, depending on which occurs first. Due to the cost of servicing, motorcycle manufacturers are trying to extend maintenance intervals as much as possible. Until a few years ago, few manufacturers scheduled intervals beyond 5,000 km (including Japanese brands). Nowadays, it is not uncommon to have the motorcycle serviced every 8,000 to 10,000 km, and this also applies to scooters. The situation is slightly different for off-road motorcycles, which require more frequent maintenance intervals. Knowing how often the "pit stop" at the repair shop is scheduled also provides a more accurate idea of the maintenance costs.
Unfortunately, when a motorcycle engine seizes, it is common for the connecting rod pieces to cause severe damage to the cylinder, piston, and crankshaft, making it impossible to use the motorcycle and resulting in very expensive repairs.
The Noise of a Seized Engine: Symptoms in Motorcycles
How to recognize when an engine is about to seize? Unfortunately, it is not possible to predict it before the damage actually happens, but it is essential to identify the early symptoms. The most critical indicator is a metallic rattling noise coming from the engine or alternatively, hearing regular knocks (similar to hammering on metal). These noises mean that there is clearance in the connecting rod's foot or head (note that the head is connected to the crankshaft, while the foot is linked to the piston). Typically, the first components to fail are the bearings in the head or the base of the connecting rod. This creates friction, increasing the engine's temperature, and consequently, the strain on the connecting rod, leading it to break easily.

Seizing the Motorcycle Engine: Risky Behaviors
Risky behaviors that may cause the engine to seize include operating the engine at high RPMs or going into over-revving for too long, such as maintaining high RPMs during a prolonged descent while keeping a low gear engaged.
To prevent engine seizing, proper lubrication with quality oils suitable for your motorcycle and regularly replacing oil filters is crucial. Athena offers a wide range of oil filters manufactured by first-tier suppliers for leading motorcycle brands, ensuring efficient filtration in all conditions of operation. It is good practice to replace the oil filter with every oil change, approximately every 10,000 km for road motorcycles (more frequently for city use) or approximately every 10 hours of use for off-road models. Changing the engine oil filter is a relatively easy job that you can do in your home garage without necessarily needing a mechanic.
The engine knocking can also be a result of a seized piston: click here to learn more about it.
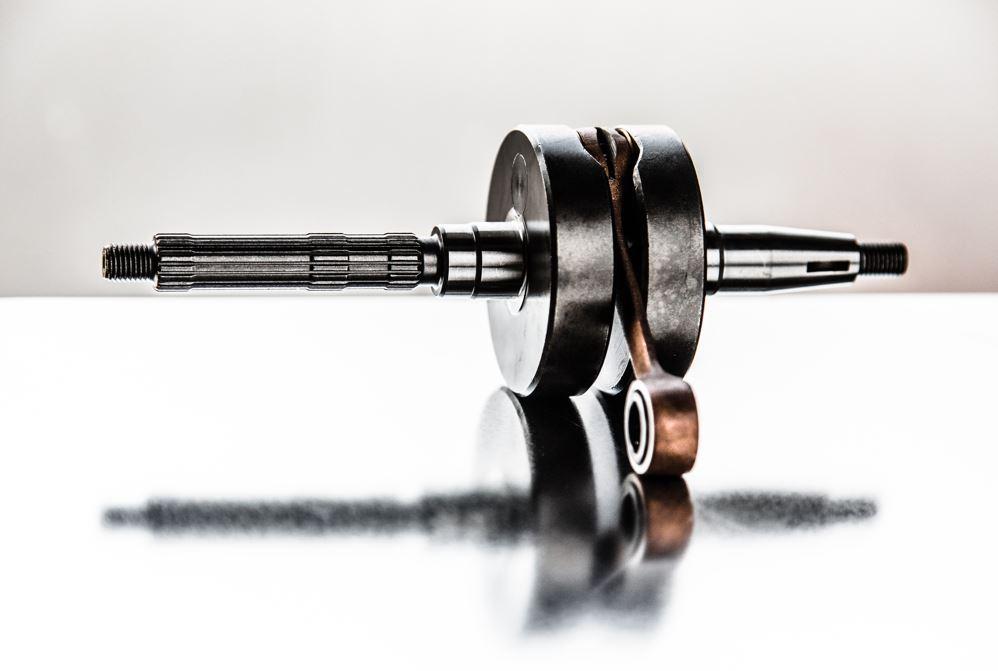

Seized Crankshaft: What to Do
Our recommendation, when you suspect a seized engine, is to stop as soon as possible and turn off the engine. The connecting rod may not be completely broken but only cracked or deformed, and it is essential to prevent damaging other engine components. If you have some mechanical skills, you can replace the connecting rod yourself; otherwise, it is best to rely on your trusted mechanic.
Athena offers high-quality connecting rods for off-road applications—lightweight and durable, ensuring excellent performance. Made from materials similar to the original components, Athena's connecting rods are designed to reduce rotating and alternating masses.
As mentioned, the damage can also be significant, and it should be noted that the cylinder head of the engine needs to be disassembled. On average, labor costs can range from 500 to 1,000 euros, in addition to the costs of replacement parts.